1. Introduction
- Define Partial Stroke Test (PST) → a method to verify valve and actuator functionality without performing a full stroke.
- Mention industries → oil & gas, petrochemical, LNG, power plants.
- State importance → part of SIL certification, functional safety, and reducing downtime
2. Why Partial Stroke Testing Matters
- Safety-critical valves (ESDV, BDV) can remain static for months/years → risk of sticking.
- PST reduces hidden failures by ensuring valves can move on demand.
- PST is required/recommended by IEC 61508, IEC 61511 (functional safety standards).
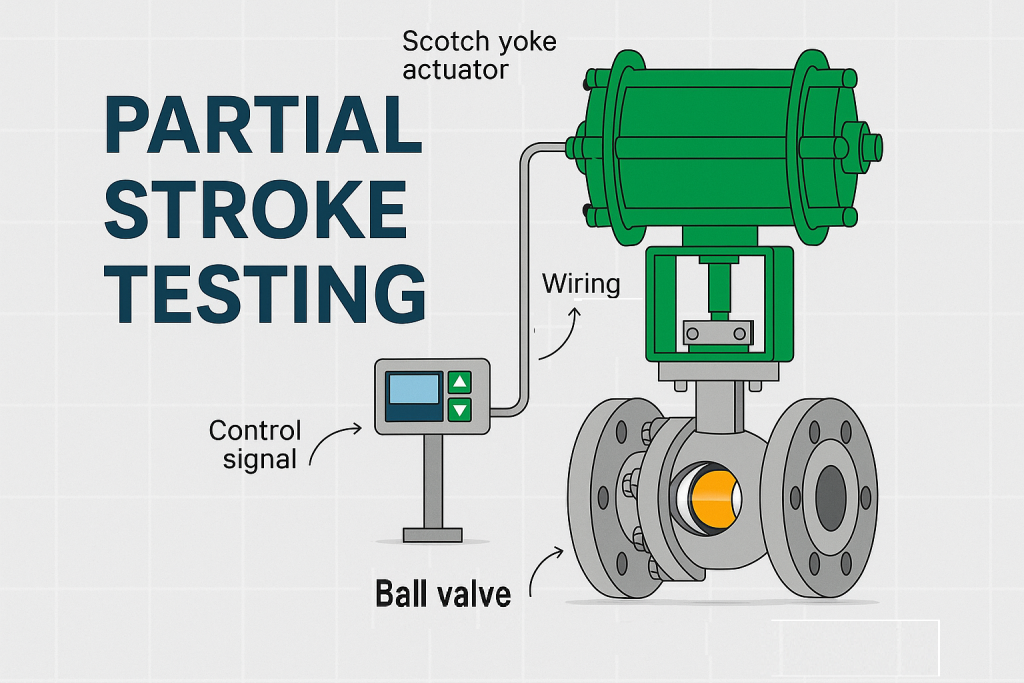
3. How Partial Stroke Testing Works
- Performed on pneumatic or hydraulic actuators.
- Valve moves only partway (e.g., 10–20% of stroke) without disrupting process.
- Results logged for predictive maintenance.
4. Benefits of PST
- Improved Safety Integrity Level (SIL) compliance.
- Reduced maintenance costs — less need for full shutdowns.
- Minimized downtime — test without halting production.
- Early detection of valve/actuator issues.
5. Technologies for PST
- Smart Positioners with PST functionality.
- Dedicated PST controllers for ESDVs/BDVs.
- Integration into Safety Instrumented Systems (SIS).
6. Challenges & Best Practices
- False positives/negatives if not calibrated.
- Must ensure PST does not impact process safety.
- Combine with full stroke tests during planned shutdowns
7. Conclusion / Call-to-Action
Partial Stroke Testing is a cost-effective and reliable way to ensure emergency shutdown valves remain functional, supporting compliance with international safety standards. Nordenflow provides actuators, smart positioners, and instrumentation solutions with PST capabilities to help clients achieve higher safety and operational reliability.
👉 Contact us to learn how Partial Stroke Testing can enhance the safety of your automation systems
